
Please wait, loading...

Please wait, loading...

![]()

Definition of Coating System
A coating system refers to a combination of multiple layers of paint applied to protect steel structures. Each paint layer, with its specific properties, plays a key role in ensuring protection. Industrial coating systems are among the most cost-effective and widely used methods for protecting steel structures, especially storage tanks and refinery facilities, against corrosive atmospheres.
Factors that reduce the lifespan of coating systems include:
Key Parameters for Applying an Effective Coating System:
Layers of a Coating System
The table below outlines 6 models of industrial coating systems, including the primer, intermediate, top coat, and protective layers:
|
No. |
Primer Layer |
Intermediate Layer |
Top Coat Layer |
Protective Layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Alkyd anti-corrosion primer |
Alkyd intermediate |
Alkyd top coat |
- |
|
2 |
Polyvinyl butyral wash primer |
Vinyl primer |
Vinyl intermediate |
Vinyl top coat |
|
3 |
Epoxy anti-corrosion primer |
Epoxy intermediate |
Epoxy top coat |
- |
|
4 |
Zinc-rich epoxy primer |
Epoxy intermediate |
Polyurethane top coat |
- |
|
5 |
Zinc ethyl silicate primer |
Epoxy intermediate |
Polyurethane top coat |
- |
|
6 |
Chlorinated rubber primer |
Chlorinated rubber |
Chlorinated rubber |
- |
Evaluation of Industrial Paint Quality
The paints listed above must be analyzed and tested according to standard procedures. Manufacturers such as Abadgaran must conduct these tests to ensure the quality of their industrial paints. Employers and contractors can refer to these test results to validate the manufacturers' claims.
Curing Time for Coating Systems
The full curing time of a coating system at 23°C and 50% humidity must not exceed 14 days.
Required Tests for Paint Evaluation:

Key Considerations in Surface Preparation and Application of Industrial Paints
Surface Preparation for Coating System Application
One of the essential prerequisites in any painting operation is surface preparation and ensuring a proper substrate condition.
Environmental conditions must be maintained throughout the surface preparation and paint application process—such as ambient temperature.
Environmental Conditions to Observe During Preparation:
Surface Conditions for Coating Application:
Before painting, contaminants such as rust, surface oxides, grease, oil, and any foreign matter must be removed. Also, surface defects such as:
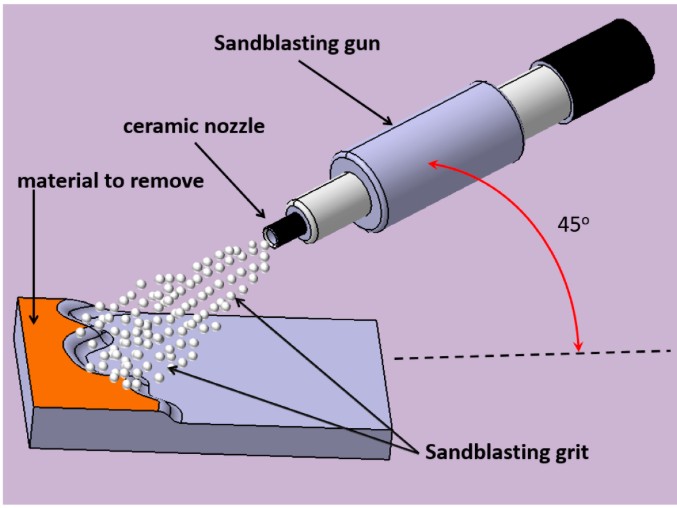
Cleanliness and Surface Roughness Standards:
The final cleanliness level depends on the type of paint used. For example, zinc-rich epoxy paints require a minimum surface cleanliness of Sa2.5. According to ISO 8501-1, corrosion grades are categorized as A, B, C, and D. If the surface falls into grade A or B, the surface profile must be 30–50 microns. If the surface is grade C or D, the profile depth should exceed 50 microns.
After surface preparation:
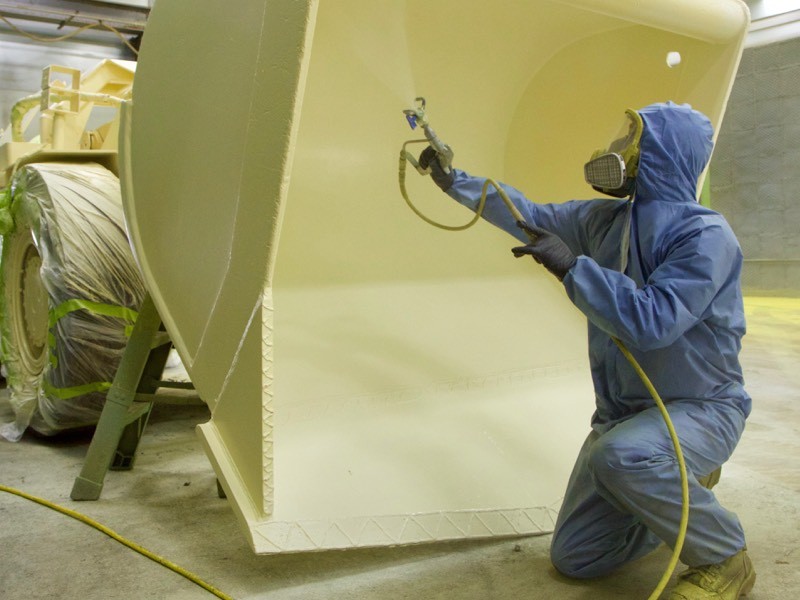
Paint Application
For zinc-rich primers:

Selection of Industrial Paints
In any coating system, the primer, intermediate, and top coats must be selected together. For example:
Curing and Drying Time
The coated system must cure for at least one week after the top coat is applied. During this time, the surface should not be used.
Layer Thickness in Coating Systems
The total thickness of the applied layers must follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. It must not be less than the recommended thickness, and a deviation of up to 20% above the recommendation is allowed. Adequate thickness enhances durability and protection.
Thinner and Viscosity Adjustments
To achieve optimal viscosity, thinners may be used. Based on the paint type, appropriate amounts can be added. Tools such as spatulas or dip viscometers can be used for measurement.
Note that adding thinner affects the volume solids percentage. Therefore, solids content must be recalculated. To achieve the desired dry film thickness, wet film thickness must also be recalculated.
This is a critical part of the painting process to ensure proper performance and longevity of the coating system.